

The treatment of a fracture depends on the type of fracture. Sometimes, your doctor might suggest a CT scan to obtain further details of the fracture, especially the joint surfaces. Your doctor might recommend an X-ray to confirm the fracture and assess displacement of the bone. The symptoms of a radial head fracture include severe pain, swelling in the elbow, difficulty in moving the arm, visible deformity indicating dislocation, bruising and stiffness. Radial head fractures can also occur due to a direct impact on the elbow, a twisting injury, sprain, dislocation or strain. The most common cause of a radius head fracture is breaking a fall with an outstretched arm. Radial head fractures are more common in women than in men and occur more frequently in the age group of 30 and 40 years.
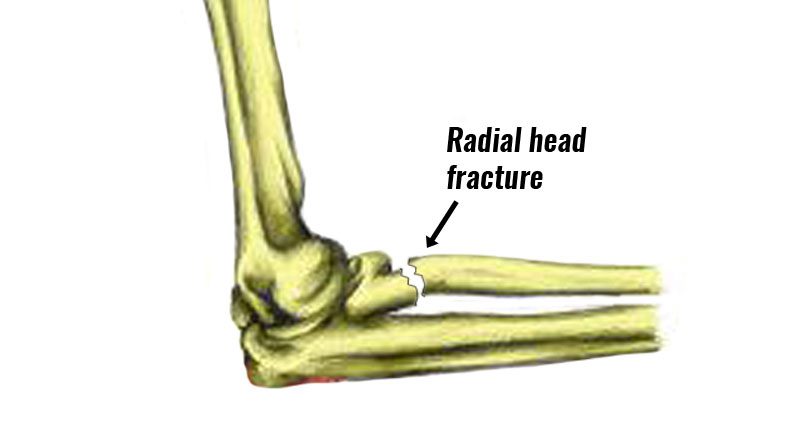
Elbow dislocations are generally associated with radial head fractures. Radial head fractures are very common and occur in almost 20% of acute elbow injuries. The injury in the head of the radius causes impairment in the function of the elbow. The head of the radius bone is cup-shaped and corresponds to the spherical surface of the humerus. The elbow joint is essential for the movement of your arms and to perform daily activities.

The elbow joint is made up of 3 bones namely the humerus bone in the upper arm which joins with the radius and ulna bones in the forearm. Open fractures, fractures that cannot be repositioned during a closed reduction, and fractures that are accompanied by nerve or vascular injuries require open surgery or open reduction and internal fixation.The elbow is a junction between the forearm and the upper arm. The pins and cast are removed after healing has begun, a few weeks after surgery. A splint is applied to protect the area for the first week, then is typically replaced with a cast. The pins are inserted through the skin, into the bone and across the fracture. In this procedure, the displaced bone fragments are repositioned during closed reduction and held in place with metal pins. If the bone fragments are displaced, surgery may be required to ensure that the fracture heals fully.Ĭlosed reduction and percutaneous pinning. Your doctor may schedule additional x-rays to make sure the bones stay in place as they heal. Your child will be given some form of sedation or anesthesia for this procedure. In this procedure-called a closed reduction-your doctor gently moves the arm to manipulate the bones back into place. In some stable elbow fractures, the bones may need to be repositioned before applying a splint or cast.
#SPLINT FOR RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE FULL#
As swelling subsides, a full cast may replace the splint. In many cases, a splint is applied to a fresh injury first. Splints provide less support than casts however, they can be easily adjusted to accommodate swelling from injuries. If the fracture is stable with no displacement, your doctor may directly apply a splint or cast to keep the bones in proper alignment while they heal. Many stable fractures heal successfully with cast or splint immobilization. Treatment for elbow fractures depends on the type of fracture and the degree of displacement. For this reason, it is important that the fracture be treated correctly at the time of the initial injury. If an elbow fracture heals in the wrong position, the elbow may remain permanently crooked and have limited range of motion. An open fracture may involve damage to the muscles, tendons, and ligaments and take a longer time to heal. When a broken bone breaks through the skin, it is called an open fracture. If the dislocation is not recognized, and only the fracture is treated, it can lead to permanent impairment of elbow joint function. A fracture of the ulna associated with a dislocation of the top of the radius at the elbow is called a Monteggia fracture. Fractures of the tip (olecranon) of the ulna are rare.įracture dislocation. Because growth plates help determine the length and shape of the mature bone, a fracture that disrupts the growth plate can result in arrested growth and/or deformity if not treated promptly.įorearm. A fracture can occur at the top (head) of the radius bone, causing it to move out of place. The upper arm bone and both forearm bones have areas of cartilage called growth plates located near the end of the bone. Rosemont, IL, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2003. Reproduced and adapted from J Bernstein, ed: Musculoskeletal Medicine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
